Spermatogenesis, the creation of mature sperm cells, takes place in the male testis from the start of puberty and continuing throughout life.
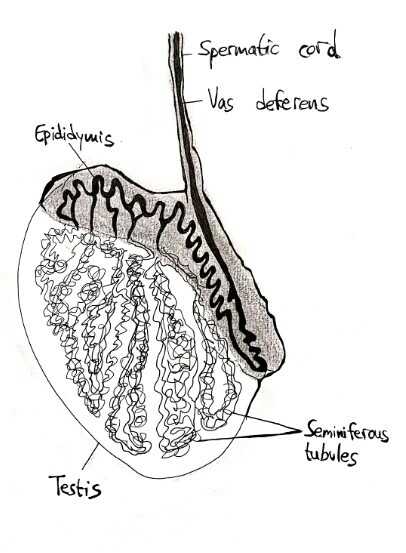
Stem cells are cells that are capable of becoming any other type of cell in the body. Some of these stem cells are found in the testis, specifically in the seminiferous tubules, and are the initial cells that divide to form the first type of early sperm cells, the spermatogonia.
These spermatogonia, while not as capable as stem cells, are able to specialize further and become spermatocytes, the next step along the way to creating a mature sperm cell.
Spermatocytes can then become spermatids, and spermatids become spermatozoa in a further process known as spermiogenesis. Mature spermatozoa are known as sperm cells, those cells which are used to fertilize the egg and produce an embryo.
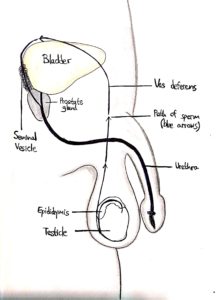
The majority of spermatogenesis occurs within the testis, while the last stage of maturation will occur in the epididymis. The mature spermatozoa will remain stored in the epididymis until ejaculation.