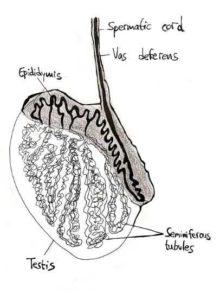
Within the oval-shaped testicle are several different bundles of cells, each of which contributes to sperm production and male sexual development in a unique way.
The seminiferous tubules take up the most space—these tiny, coiled tubes are the place where spermatogenesis, or the generation of new sperm, takes place.
The tubes are lined with Sertoli cells, which provide developing sperm cells with support and nourishment as they grow. They also release a protein that increases the amount of testosterone in the seminiferous tubules, which then helps with spermatogenesis.
Another cell type found in the testes are Leydig cells. The main role of Leydig cells is the production of male hormones, critical for spermatogenesis, and sexual development.
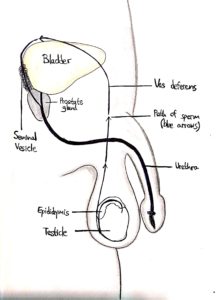
Once the sperm cells have been formed, they must be transferred to the epididymis, where they will become fully mature and be stored.